Section 2 bending
First, the bending process
1, elastic bending stage. The sheet material undergoes bending deformation under the action of external bending moments, first through the elastic bending stage.
2, plastic bending stage. With the increase of the external bending moment, the bending deformation of the plate increases, and the inner and outer skin metals reach the yield limit first, and the plate begins to transform from the elastic deformation stage to the plastic deformation stage.
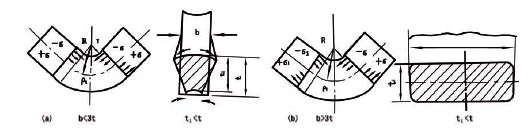
3, the characteristics of the bending deformation process
1 The deformation zone is mainly located in the rounded part of the bending part, but no deformation occurs in the two sections far from the fillet area.
2 In the bending deformation zone, the tangential metal in the outer zone is stretched, and the tangential metal in the inner zone is compressed short. In these two deformation zones, there is a layer of metal with the same length, ie a strain-neutral layer.
Second, the minimum bending radius
1. The position of the strained neutral layer. When stamping the sheet material, the position of the strain-neutral layer must be determined in order to determine the minimum fillet radius of the punch and the blank size of the bent part.

2, the determination of the minimum bending radius. During the bending process, the fiber of the outer layer of the material is subjected to tensile stress. When the thickness of the material is constant, the smaller the bending radius, the greater the tensile stress.
Third, bending rebound phenomenon
1, the calculation of the rebound value. When the bending deformation is not affected by the external force, it is always accompanied by elastic deformation, so that the bending center angle and the bending radius become the same as the size of the mold, which is called rebound.

2, factors that affect the amount of rebound
1 Mechanical properties of material 2 Bending deformation degree 3 Bending center angle 4 Bending method 5 Workpiece shape 6 Mold structure
3, reduce the rebound measures
Fourth, the bending process
The processability between bends refers to the requirements for the shape, size, and precision of the bent workpiece, and whether the material selection and technical requirements are in compliance with the technological requirements of the bending process.
1, the bending radius of the bending piece
2, the shape of the curved piece
3, the distance between the edge of the bending part 4, the straight edge height of the bending part
5, design process, slot

The third section of the principle of stretching
The flat blank is passed through a drawing die to form an open cylindrical or other cross-sectional shaped part, or a cylindrical or other cross-sectional shaped blank is reworked into a cylindrical or other cross-sectional shaped part, and this process becomes deep drawing (or drawing) ).
First, deep drawing process
1, the die mouth flange section. This part of the material under the joint action of radial tensile stress and tangential compressive stress, the material plastic deformation and gradually into the die.
2. In addition to the radial tensile stress and tangential compressive stress in the above-mentioned area, the material of the corner portion of the die is also subjected to compressive stress resulting from pressure, friction, and bending at the corner of the die. Transition zone.

3, the wall part. This part of the material has become cylindrical, the material will not have a large deformation.
4, punch corner section. This part of the material withstands the radial and tangential tensile stresses of the punch radius. It also withstands compressive stresses in the thickness direction due to pressure and bending of the punch fillet.
5, the bottom part of the tube. In addition, the material remains flat during deep drawing without large deformation, but due to the effect of the tensile force of the punch, the material undergoes two-way tensile stress and becomes slightly thinner.
Second, the mechanical analysis of the deep drawing process
1, the stress distribution of the flange deformation area

2, wrinkling phenomenon analysis

3, cracking problem analysis
4. Main measures to overcome cracking and wrinkling
1 The main measures to prevent cracking 2 The main measures to prevent wrinkling
Third, deep drawing coefficient and drawing times
When drawing up the deep-drawing process and designing the deep-drawing dies, it is necessary to determine in advance whether the parts can be deepened or deep-drawn
1, deep drawing coefficient
2, factors affecting the draw factor
3, deep drawing
4. Deep drawing methods after the first deep drawing
Fourth, the drawing process and stretching process calculation
1, drawing parts process requirements
2, drawing process calculation










